Summary Diagram: Getting to Grips with the Constitution
18th August 2015
Getting to Grips with the Constitution
The UK Constitution tells us about:
- The length of time between elections
- Who is eligible to vote
- The rights and duty of the citizen
- The extent and the limits of government and parliamentary power
- The powers of the judiciary
- The manner in which governments are formed
- The role and powers of parliament
- The role and powers of the Queen and Prime Minister
- The relationship between national, regional and local government
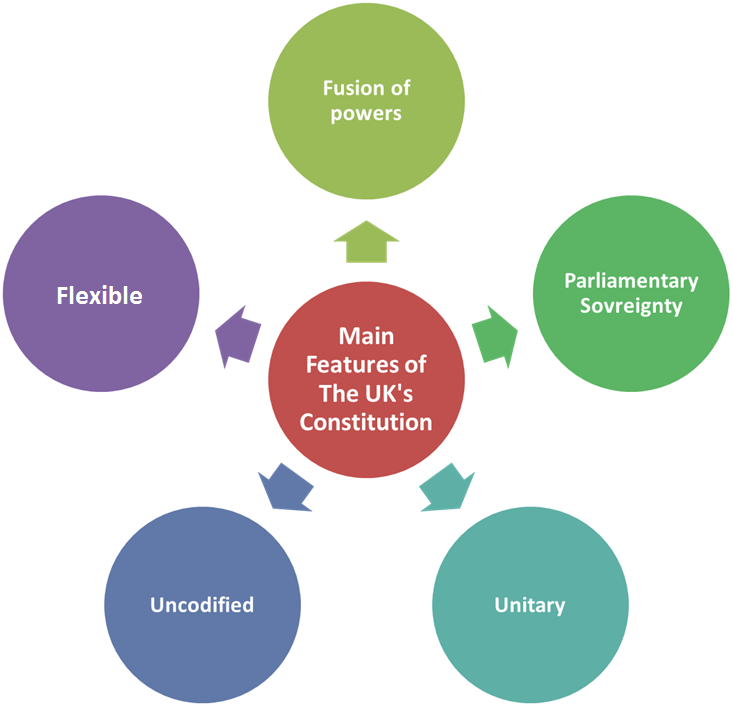
Core Institutions
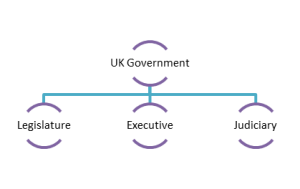
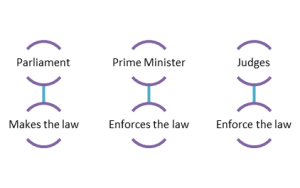
Fusion of powers
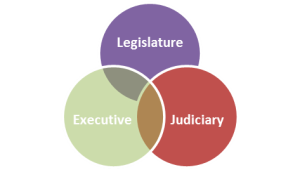 The legislative, executive and judicial functions overlap.
The legislative, executive and judicial functions overlap.
The overlap between the legislative and executive functions relates to those individuals who are both Members of Parliament and members of the executive, in other words government ministers.
Another overlap occurs between the legislature and judiciary. This relates to the Law Lords, the senior judges who also sit in the House of Lords.
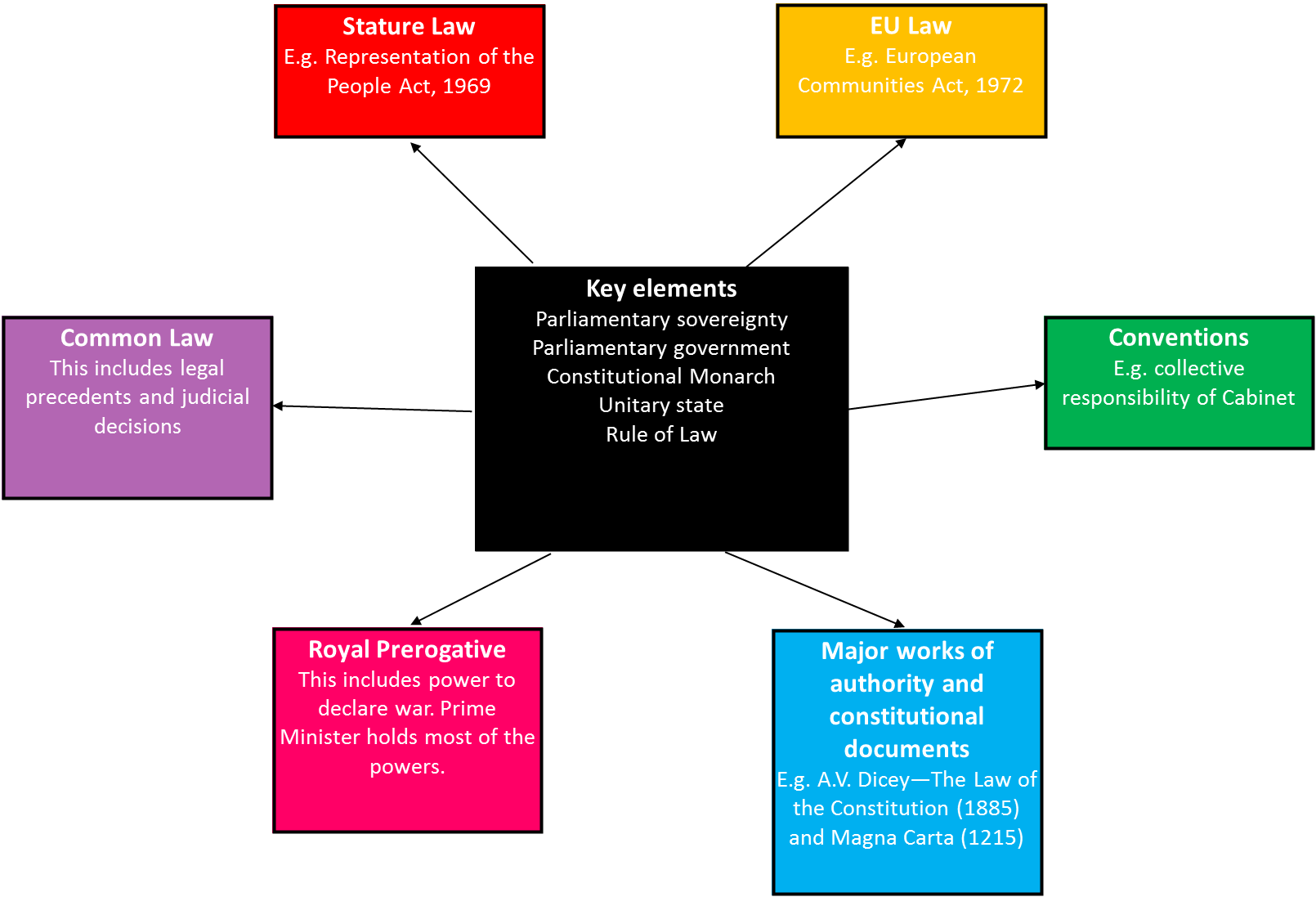
Types of Constitution
Codified = A codified constitution is a constitution in which key constitutional provisions are collected within a single document, it is commonly known as a written constitution.
Uncodified = An uncodified constitution is a constitution that is made up of rules that are found in a variety of sources, in the absence of a single legal document or written constitution.

0 Comments