What determines supply?
1. The price of the product
The price that consumers are willing to pay is, obviously the most important factor affecting the level of supply, and changes in the price that the producer can get for his product will move supply along the existing supply curve (this is known as an extension or a contraction in supply).
2. The cost of production
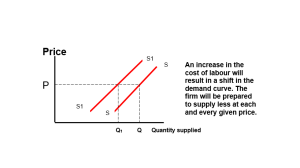
The cost of inputs will affect all types of production. If input prices rise, then the business’s level of profitability will change and the amount of goods and services which the firm is willing to produce will change.
3. The objectives of the producer
Many producers are not, surprisingly enough, interested in making the maximum profit. They may prefer to make a satisfactory profit. This simply may be sufficient profit to give a reasonable return on the money invested and provide the producer a reasonable living without incurring the risks associated with expanding the business. In such a case even a price rise might not be sufficient to encourage the business to expand its production.
4. The technology which is available
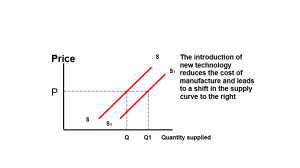
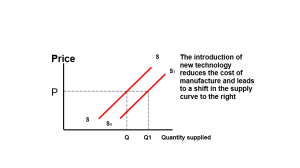
The level of available technology will influence the level of supply. If a new process is introduced, or new production machinery is developed, suppliers may be willing to increase the level of production, even though the price, which can be, charged remains the same. The introduction of new materials may have the same effect. For instance, the availability of man-made fibre has increased the willingness of shirt manufacturers to produce at a relatively low price.
5. The influence of government
Government may be influential in promoting or discouraging certain goods. An increase in the tax placed upon cigarettes may discourage the production of cigarettes as demand is reduced.